Change management strategies for successful ERP implementation
Synopsis
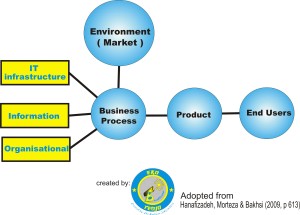
In this paper provides some arguments build about Change management strategies for successful ERP implementation. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a system integration tool to assist an organisation at particular organisational areas in share data and knowledge, cost-saving, and business process performance. Generally, ERP system provides efficiency and effectiveness of system integration across organisation’s functionality, such as finance and accounting, marketing, sales, production, logistics, freight, and many more. An ERP system is suitable for all business processes. On the other hand, there is a failure system in some ERP. Many organisations face some difficulties in workers’ resistance to change an ERP system. They can implement ERP system effectively by promoting the strategies of Change Management in the workplace. This purpose of this paper is to show synchronising the strategies of Change Management and ERP implementation in overwhelming the user resistance to change.
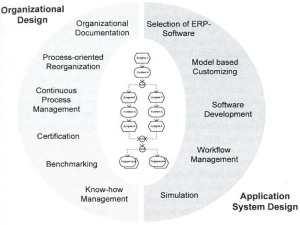
Aladwani (2001) asserted, “Some of the technical strategies that have been proposed to determine ERP success.” There are two most critical marketing research streams are strategic marketing and consumer behaviour. There are three phases of framework process-oriented in workers’ resistance to ERP implementation, such as:
- Knowledge formulation
- Strategy implementation
- Status evaluation.
Critiques
Generally, many workers will shock from something change in their workplace, and most of them feel comfortable with the existing system and they think they need to some efforts to learn. Rabaai (2009) assert that “Resistance to new technology is a noted phenomenon in many cultures, but is one that requires effective change management strategies driven from the top.” Change Management plays the core roles in successful ERP implementation. Epicor (2012) stated, “Employees need to be introduced to new processes and job roles over a period of time so that they can accept and internalize these developments.”
Reflection
This is some Aladwani’s best work. Notwithstanding this article quite old for today’s research, this article is good and can also be used as a reference for beyond research paper.
REFERENCES
Aladwani, A.M. 2001, ‘Change Management Strategies For Successful ERP Implementation’, Business Process Management Journal, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 266–275.
Epicor 2012, Best Practices for ERP Implementation [White Paper], Dublin, California: Epicor Software Corporation.
Rabaai, A. 2009, ‘THE IMPACT OF ORGANISATIONAL CULTURE ON ERP SYSTEMS IMPLEMENTATION: LESSONS FROM JORDAN’, viewed 30th September 2013, http://eprints.qut.edu.au/29838/1/THE_IMPACT_OF_ORGANISATIONAL_CULTURE_ON_ERP_SYSTEMS_IMPLEMENTATION.pdf
<< Back to introduction page.